The ratio of electric vehicles to charging points in California is so large that it has become an elephant in the room. State officials will have to build a large distribution of charging stations for 7 million electric vehicles in California. Experts and lawmakers are confounded by the unprecedented rate at which the population of electric vehicles in California is growing.

It has been suggested that California would need roughly one million charging stations by 2030. To put this figure into perspective, drivers currently have access to less than 100,000 public chargers as of December 2023. So, to meet the one million projection, the state would need to build a minimum of 129,000 new charging stations every year for the next seven years.
California is not resting on its laurels concerning the construction of public chargers. However, that goal is quite lofty, and most stakeholders agree it is unrealistic. California has just over 8,000 gas stations for its combustion engine vehicles, but those were not built in seven years. Indeed, we reckon it took more than 15 years to build all those gas stations. Nonetheless, the lofty charging station target is what California needs to reassure drivers that there will be enough public chargers to meet the electric vehicle population.
What Is the Electric Vehicles Rule in California?
The state of California has reeled out an ambitious electric car mandate. This is thanks to the poise of Governor Gavin Newsom’s administration about the climate change agenda. Gov. Newsom has instituted a rule stipulating that 68% of all new 2030 model cars to be sold in the state must have zero emissions. The mandate will raise the zero-emission bar to 100% by 2035. Experts project that California would host 15 million electric cars by that date.

While the mandate is very plausible and visionary, concerned stakeholders have faulted the timeline. For example, Professor Bruce Cain of Standford University was involved in formulating a policy brief highlighting California’s scarcity of charging points. Cain submitted, “This is a wakeup call that we address potential institutional and policy obstacles more seriously before we commit blindly.”
Democratic lawmaker Jesse Gabriel, who represents Encino, has also harped on issues similar to those at Stanford University. “We are Going to look really silly if we tell people that they can only buy electric vehicles, and we don’t have the courage to support that.”
California faces hurdles in scaling its effort to sustain the growing population of electric vehicles in the state. For example, taxpayer money cannot finance the charging stations alone. Instead, a private-public partnership would be required. Similarly, the power grids will need major upgrades before they can shoulder the weight of the charging stations’ hefty power consumption.
Is Charging an Electric Car Cheaper Than Gas in California?
If the electric vehicle in question is to operate within California, the cost of charging an electric car would be way cheaper than filling up on gas. However, this conclusion is not applicable in other states. Here’s why. Despite the noised deficits, California still has one of the US’s largest densities of public charging stations.

According to a recent auto-vs-EV review by CNET, even in California’s backwoods, where energy rates are sky-high, charging electric vehicles remains cheaper than running on gas.
What Is in Electric Vehicles?
Electric vehicle propulsion comes from electric-powered motors, which are sustained by juice from an onboard array of batteries. A few years ago, the batteries required to power electric vehicles accounted for a large percentage of their payload. However, recent improvements in battery technology have made the arrays more compact and car ranges longer. This breakdown highlights some of the advantages of electric vehicles. They save on fuel, reducing the user’s carbon footprint.
ALSO READ: Here Are the 12 Most Eco-Friendly Cars To Buy in 2024, 5 of Them Are Not Even Electric Vehicles
How Do Electric Cars Work?
Electric vehicle technology can be broken down into simple synchronous operations, though most EV systems are complex. The electric vehicle receives energy from a charging station or an electric vehicle charger and stores it in an onboard array of batteries. The stored energy powers the electric motor(s), which in turn drives the wheels.
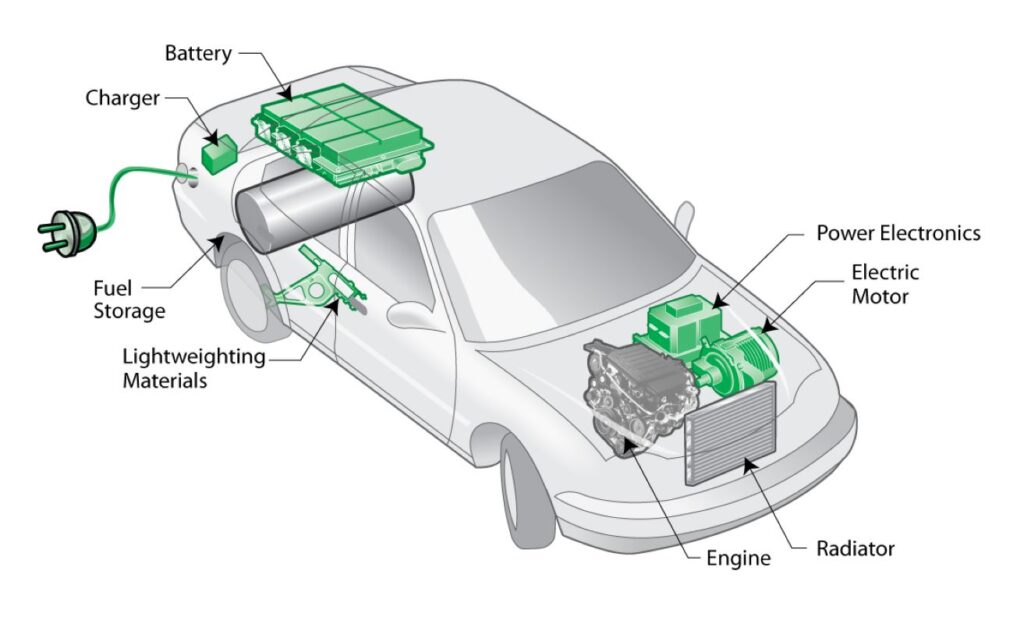
The circuitry is designed so that the accelerator sends signals to the power controller to control the speed of an electric vehicle. The power controller adjusts the frequency of AC power coming from the inverter.
ALSO READ: Unwanted and Unworkable’: Harris’ Electric Vehicle Plan Faces Setback After Automaker Reversal
The Most Popular Electric Car Brands
Chinese electric vehicles seem to be taking over the EV market as the Asian electric car brands offer cheaper prices. However, if we are to look away from annual sales and revenue, the Tesla brand remains the most popular electric vehicle maker.

BYD remains China’s most popular electric vehicle brand, at least in the international market.
You Might Also Like:
Kohl’s Focuses on Cost Controls and Leaner Inventories to Boost Profit Targets
Starbucks Rushes to Win Back Customers Amid Falling Sales
Why Gold Has Been Outperforming Most Other Assets This Year
Volkswagen China Spends a Lot of Time With Xpeng To Develop New EVs
Eli Lilly Launches a New, Cheaper Version of Weight Loss Drug Zepbound to Improve Access and Supply

