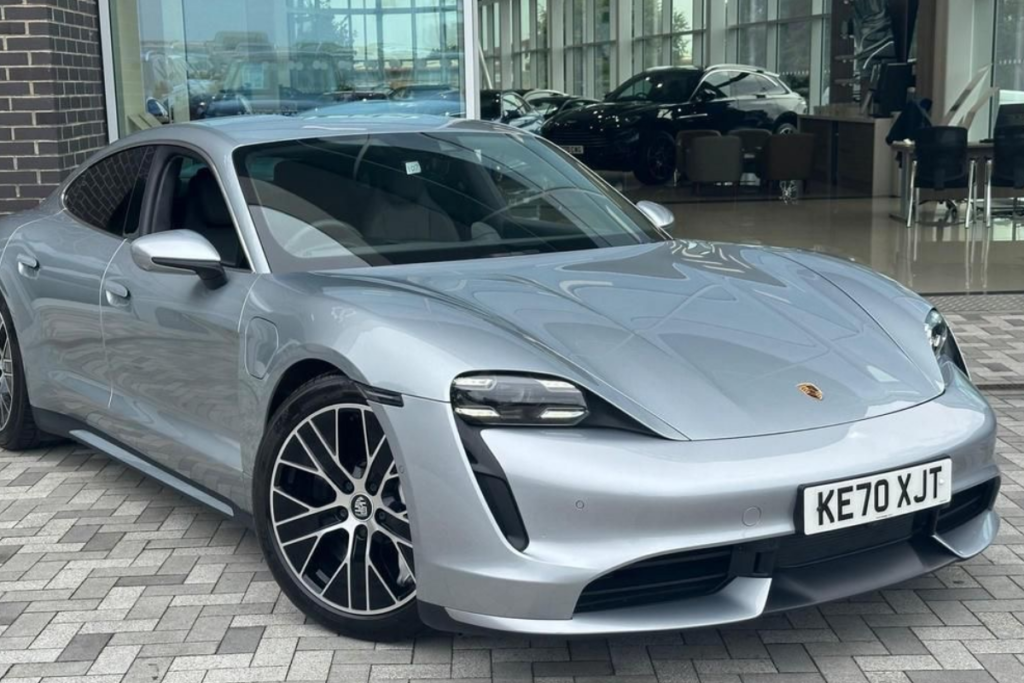
Porsche electric vehicles (EVs) are heavy mainly because of the large batteries and other high-performance components. However, when the Porsche Taycan Turbo’s Official EPA figures came out, people were surprised to see that it could only cover a range of 201 miles on a single charge. This is average compared to other electric cars.
The car’s efficiency, that is, how well it uses energy, was the worst in its class. Although performance cars are not the best type for saving energy, it is different if they are electric cars. Jason Fenske explained this in a video on his YouTube channel, Engineering Explained.
Fenske said that while electric car engines are usually very efficient at using power, batteries cannot hold as much energy as regular gas tanks. This means that if the car is not efficient and uses power quickly, a much bigger, heavier battery will be needed to compensate.
The Reason Why Porsche Electric Vehicles Are Heavy
The Porsche Taycan Turbo needs a big battery to drive long distances. It requires a 93.4 kWh battery to drive 201 miles. Meanwhile, the Tesla Model S has a more efficient system that can go much further. The Tesla’s long-range can go 373 miles with a slightly bigger battery of 100 kWh.

Even though Tesla can travel almost twice as far, the Porsche still has nearly the same battery weight. To improve the range of the sports car, you would need to add a lot more weight to the batteries. In fact, according to Fenske‘s calculations, the Porsche will need to add an extra 1,189 pounds of battery to match the Tesla Model S’ range driving range.
In addition to this fact, the Porsche is already heavier than the Tesla. Even with a smaller battery, the Porsche weighs about 5,132 pounds, which is 249 pounds heavier than the Tesla. While Porsche has done a great job of making sure the car still performs well despite its weight, having a heavier car affects its performance in almost every way. If the Porsche’s motors were more efficient, it would perform even better.
Reason Why Porsche EV Does Not Have a Long Range
There is a reason why some electric cars, like the Porsche, do not have as much range as Tesla. One primary reason is that the companies that make cars like Porsche or Audi do not let drivers use the full capacity of the car battery. For example, in the Porsche Taycan, about 12% of the battery is blocked off. This means you cannot use it as a driver.
These automakers do this because charging a battery to 100 percent repeatedly can wear it out faster. Therefore, limiting how much battery a driver can use helps the battery last longer. On the other hand, Tesla lets drivers use the full battery. However, they recommend not doing this every day.
The company says the best thing to do is to save the battery for long trips, giving drivers more control over their battery usage. However, companies like Porsche probably do not trust drivers to take care of the battery in the long run, especially since their warranties last about eight years.
For Porsche, even if the Taycan Turbo Model could use the entire battery, it still would not get as much range as the Tesla Model S. Tesla cars are more efficient and weigh less. This helps them go farther on a full charge.
ALSO READ: China’s Electric Car Competition Shifts Focus to Chip Technology as Tech Becomes Key Differentiator
Why Are EVs Lithium-ion Batteries So Heavy?
Lithium-ion batteries are heavy because they need to store a significant amount of energy to provide enough driving range for electric vehicles. EV batteries are also heavy because they need to hold a lot of energy to enable an electric car to drive long distances. The amount of energy stored in a lithium-ion battery, known as energy density, is still lower than other energy storage technologies.
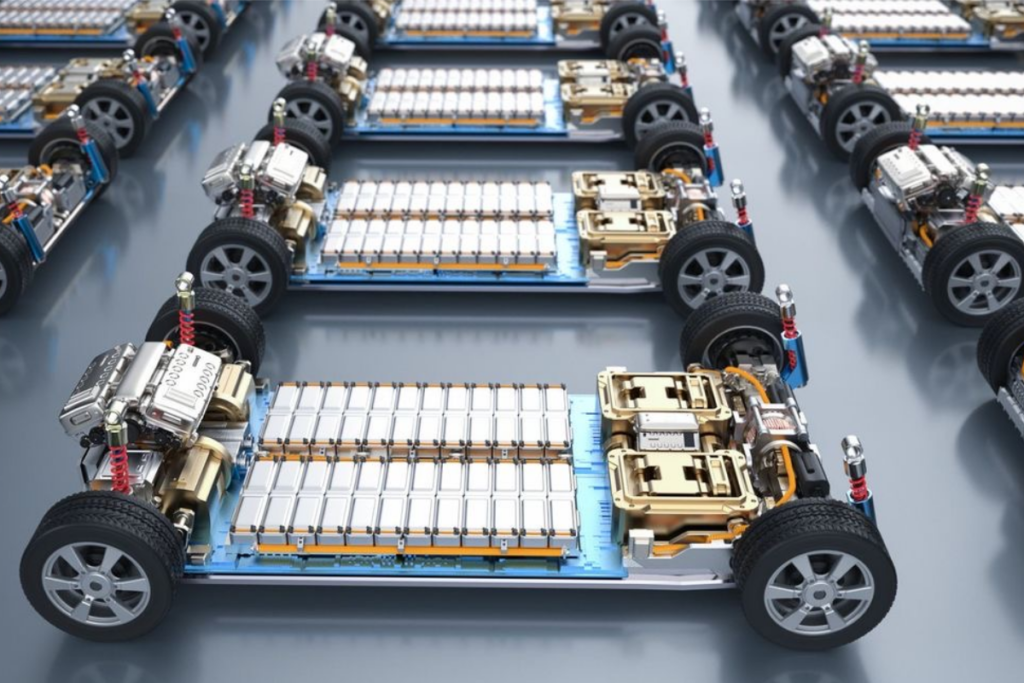
As a result, lithium-ion batteries need to be bigger and heavier to hold enough power to make electric cars practical for everyday use.
ALSO READ: Here Are the 12 Most Eco-Friendly Cars To Buy in 2024, 5 of Them Are Not Even Electric Vehicles
Can Automakers Create Lighter, More Energy-Efficient Batteries Without Sacrificing Power?
Automakers can create more energy-efficient batteries without sacrificing power, and they are working hard to achieve that. However, there are some challenges. Although automakers are making progress, it is a slow process. Making lighter EV batteries without losing power is still a significant technical challenge.

EV batteries are heavy because they store much energy, enabling cars to cover long driving ranges. Scientists and engineers are exploring new materials and designs that can hold more power in smaller packages to make these batteries lighter.
One primary goal is to improve energy density. This means packing more energy into each unit of weight. Some companies are experimenting with solid-state batteries, which could be lighter and more efficient than the current lithium-ion batteries.
A solid-state battery uses solid materials instead of the liquid electrolytes found in regular batteries. They could store more energy and be safer to use. Another approach is the use of different materials for the battery components.
Companies could use silicon instead of graphite in the battery’s anode, which could help reduce weight while increasing power. Automakers also try to make EV batteries lighter using lightweight materials like aluminum or carbon fiber. Time will tell if they can achieve this.

